Turmeric – A Powerful Natural Anti-Inflammatory Remedy
Turmeric has gained global recognition in recent years and is frequently described as one of nature’s most powerful healing herbs. It has been associated with support for a wide range of health conditions, from cancer-related research to chronic skin disorders such as psoriasis. Among its most valued qualities are its exceptionally strong anti-inflammatory properties.
One of the key advantages of turmeric is its high level of safety. Adverse effects are extremely rare, especially when compared with conventional pain-relief medications like ibuprofen, which are known to increase the risk of stomach irritation and internal bleeding.
Top 10 Anti-Inflammatory Benefits of Turmeric
Below are ten evidence-based health benefits linked to turmeric and its active compound, curcumin.
1. Reduced Risk of Heart Disease
Heart disease remains the leading cause of death worldwide, making prevention a critical priority. Curcumin has demonstrated the ability to counteract several factors that contribute to cardiovascular disease, including elevated cholesterol levels and impaired endothelial function.
Endothelial dysfunction plays a major role in heart disease, as the endothelium regulates blood pressure, clotting, and vascular health. Research indicates that curcumin reduces oxidative stress and inflammation, and one study found its effectiveness comparable to the cholesterol-lowering drug Atorvastatin.
Additional findings suggest that consuming approximately one teaspoon of turmeric daily may lower the risk of heart attacks to a degree similar to performing three 60-minute cardiovascular workouts per week.
2. Lower Cancer Risk
Curcumin has been widely studied for its potential role in cancer prevention and supportive therapy. Scientific evidence shows that it can influence cancer development, growth, and spread at the molecular level.
“A number of laboratory studies on cancer cells have shown that curcumin does have anticancer effects. It appears capable of destroying cancer cells and preventing further growth, particularly in breast, bowel, stomach, and skin cancers.” – Cancer Research UK
Research suggests that curcumin may:
- Promote the death of cancerous cells
- Reduce angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels in tumors)
- Limit metastasis (spread of cancer)
3. Powerful Anti-Inflammatory Effects
A study published in the journal Oncogene compared a wide range of natural anti-inflammatory compounds with common pharmaceutical NSAIDs. Curcumin was identified as the most potent anti-inflammatory agent, outperforming aspirin and ibuprofen.
Chronic inflammation is now recognized as a root cause of many modern diseases, including arthritis, ulcerative colitis, fibromyalgia, and cancer. Turmeric’s anti-inflammatory properties also support wound healing, sciatic nerve pain relief, post-operative recovery, and joint health.
4. Supports Weight Management
Research published in the journal BioFactors indicates that curcumin may help reduce the growth of fat cells. The study found that its anti-inflammatory properties effectively suppress inflammatory processes linked to obesity and its related health complications.
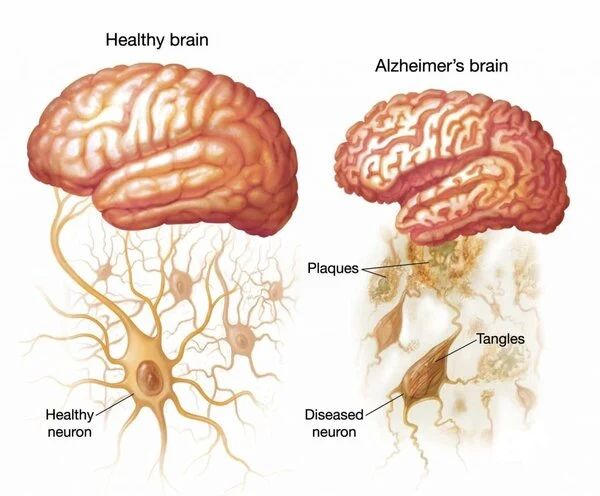
5. Alzheimer’s Disease Prevention and Support
The anti-inflammatory properties of turmeric are being explored as a potential approach for Alzheimer’s disease support. Curcumin is capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier, which allows it to interact with amyloid plaques commonly found in the brains of individuals affected by Alzheimer’s disease.
6. Natural Antidepressant Properties
Numerous studies have demonstrated positive effects of curcumin in the management of depression. Curcumin influences neurotransmitter activity through its interaction with brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF).
A human study published in Phytotherapy Research compared curcumin, Prozac, and a combination of both in individuals with major depressive disorder. After six weeks, curcumin proved to be as effective as Prozac. Combining both resulted in slightly improved outcomes, though not statistically significant.
The study concluded that curcumin may serve as a safe and effective option for individuals with mild depression.
7. Enhances Skin Health
Curcumin offers notable benefits for skin health, particularly when applied topically. A study involving 814 participants showed that turmeric paste successfully treated 97% of scabies cases within 3 to 15 days.
Turmeric also accelerates the healing of acne-related wounds, helps reduce scarring, calms pores, minimizes breakouts, and supports the management of psoriasis flare-ups.
8. May Support Diabetes Management
Curcumin has shown promising results in diabetes-related research. One study found curcumin to be significantly more potent than metformin in activating AMPK, an enzyme crucial for metabolic regulation.
Researchers consider AMPK a therapeutic target for type 2 diabetes. By activating this enzyme, curcumin shows strong potential for reducing insulin resistance and supporting metabolic health.
9. Supports Natural Detoxification
Curcumin is a powerful antioxidant capable of neutralizing free radicals responsible for oxidative damage. It also enhances the activity of the body’s own antioxidant enzymes, providing valuable support to liver function.
10. Brain Health and Neuroprotection
Multiple studies have examined curcumin’s role in supporting brain health. Beyond Alzheimer’s disease, turmeric has been studied for its potential benefits in Parkinson’s disease and stroke recovery.
Turmeric also contains aromatic-turmerone, a compound studied for its influence on neural stem cells. Research from Germany found that exposure to ar-turmerone increased neural stem cell numbers by up to 80%, suggesting promising potential for brain regeneration.
The Best Way to Consume Turmeric
To maximize turmeric’s benefits, it should be consumed alongside black pepper and a source of healthy fats such as coconut oil or avocado. Studies show that piperine from black pepper can increase curcumin absorption by over 2,000%, with fats further enhancing this effect.
References
- Hewlings SJ, Kalman DS. Curcumin: A review of its effects on human health. Foods, 2017. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5664031/
- Aggarwal BB, Harikumar KB. Potential therapeutic effects of curcumin, the anti-inflammatory agent. International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 2009. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19539753/
- Jurenka JS. Anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin. Alternative Medicine Review, 2009. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19594223/
- Kunnumakkara AB et al. Curcumin inhibits proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis, and metastasis of different cancers. Cancer Letters, 2008. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18359099/
- Anand P et al. Bioavailability of curcumin: problems and promises. Molecular Pharmaceutics, 2007. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17999464/









Comments